Adding and managing Tables in your Lightdash project

In Lightdash, everything you need for BI is written as code in your dbt project. You use dbt to transform all of the data from your data warehouse, then you use Lightdash to explore it.
So, to add an manage Tables in Lightdash, we use dbt.
We'll walk you through the steps of installing + using the Lightdash CLI and generating the .yml you need to add a new table to your dbt project.
New to dbt? If you haven't used dbt before, follow dbt's getting started guide before proceeding with setting up Lightdash.
What are Tables?
Tables are the starting point to any data exploration in Lightdash - they're the data in Lightdash that you can query. The beauty of Lightdash is that we're pretty well synced with your dbt project. So, in Lightdash, Tables actually come from dbt models that have been defined in your dbt project's .yml files.
If your dbt model has been defined in a .yml file, it will appear in Lightdash as a Table.
Not sure what a .yml file is? Make sure to check out dbt's docs to learn more about building .yml files for your dbt project.
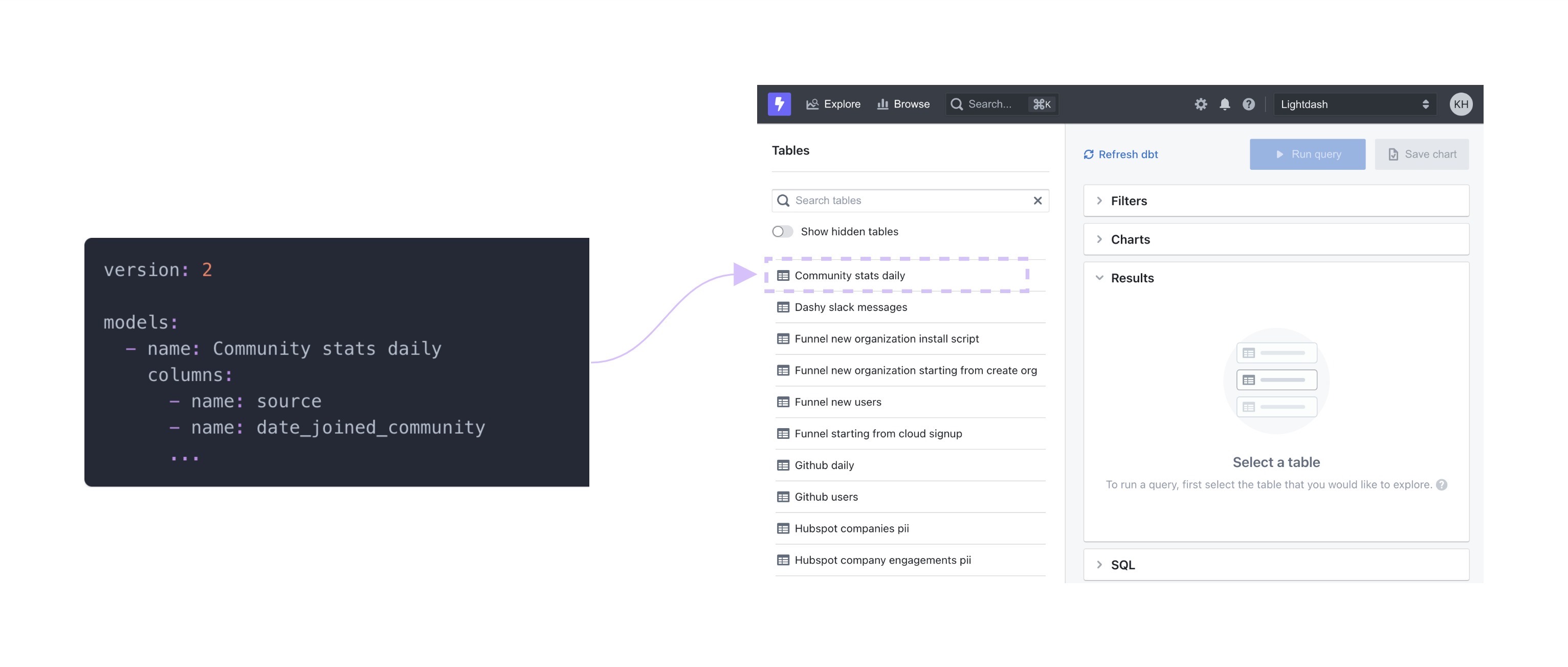
Here's an example of our Community stats daily model we've defined in dbt. In Lightdash, we can see it in our list of available Tables to explore.
Adding Tables to your Lightdash project using the CLI
Step 1. Install the Lightdash CLI tool (if you haven't already)
The Lightdash CLI is the recommended way to develop your dbt + Lightdash project. It makes development faster and easier, as well as giving you options for building more powerful automation to manage your Lightdash instance.
If you haven't installed the Lightdash CLI yet, then follow this guide to installing and setting it up, then come back to these docs once you're ready!
Step 2. Add Tables to Lightdash using lightdash dbt run -s my_model
Before you get started with the next steps, you might want to check out onto a new branch if you're working with a version controlled project!
To get a model in dbt Lightdash-ready, we need to define all of the columns that we want to explore in Lightdash. We've made this really easy to do using our CLI tool and the command:
lightdash dbt run -s my_model
This will generate the Table and dimensions for the model you've selected. It will document all of the columns in your model and these are what we explore in Lightdash as Dimensions.
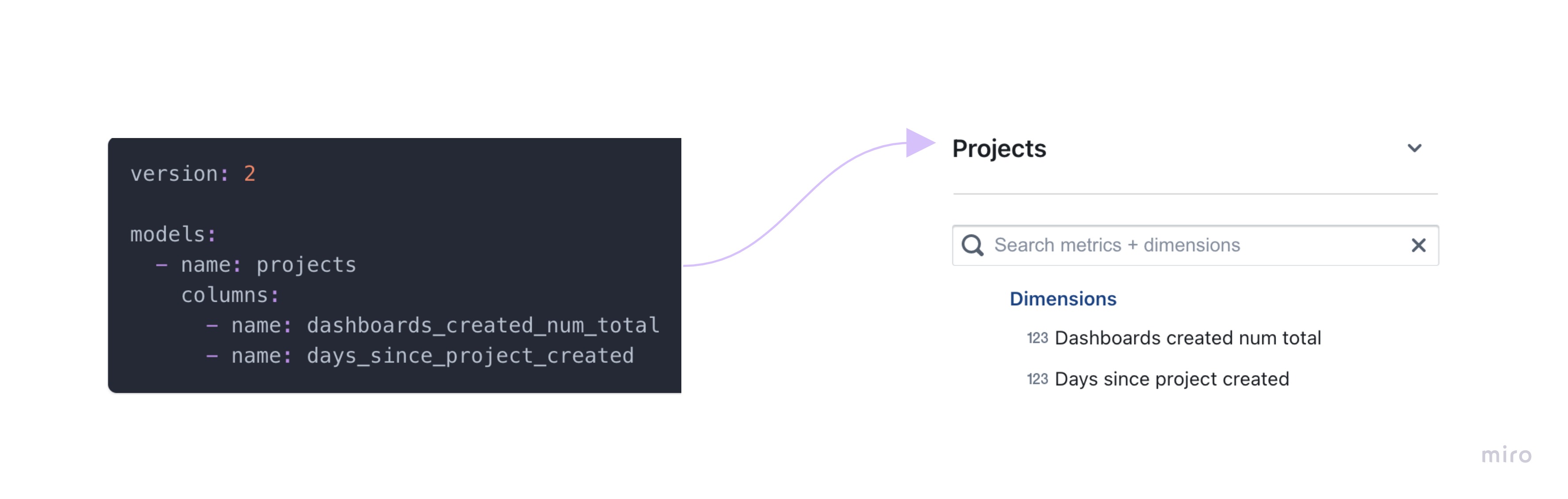
For example, if I ran lightdash dbt run -s projects, we would get:
- a
projects.ymlfile generated in our dbt project - in Lightdash, we'd have a Table called
Projects - our
Projectstable would have the dimensions:Dashboards created num totalandDays since project created.
Step 3. Preview your changes using lightdash preview
Once you've generated your Tables in dbt, you can test them out in a Lightdash preview environment.
Developer previews are temporary Lightdash projects where you can safely experiment with your metrics, dimensions and charts without affecting your production project.
So, let's spin up a developer preview and check out our changes. In your terminal, run the commands:
lightdash preview
You can read more about Lightdash preview environments here.
Step 4. Make sure your changes are in production, then you're ready to explore!
If you're working with a version controlled project, make sure to merge your changes into production (e.g. main or master).
If you're working with a local project that isn't version controlled, you don't need to worry about syncing your changes.
Once you've merged your changes, you'll want to deploy them to production. To do this, just run these commands in your terminal from your dbt project:
git checkout main # checkout main or master - or whatever your production branch name is
git pull
lightdash deploy # --target prod. If you use developer profiles in your dbt project, you might need this flag. See below.
This will deploy the changes in your dbt project to the Lightdash project you set up on your CLI tool earlier.
Note: Lightdash's deploy command will deploy using your default dbt target unless you specify to use a different target. For example, if you've set up a developer profile where it targets a dev dataset (like dbt_khindson.my_model_names), then you'll need to pass the production target in your lightdash deploy command. Something like: lightdash deploy --target prod.
Now, your Table is Lightdash-ready: so, open up Lightdash and your Table should pop up in your project!
Configuring which Tables appear in your Lightdash project
Sometimes, there are models in our dbt project with .yml files that we might not want to appear in Lightdash (base tables, I'm looking at you 👀). So, we've made it possible for you to configure which Tables you want to appear in Lightdash.
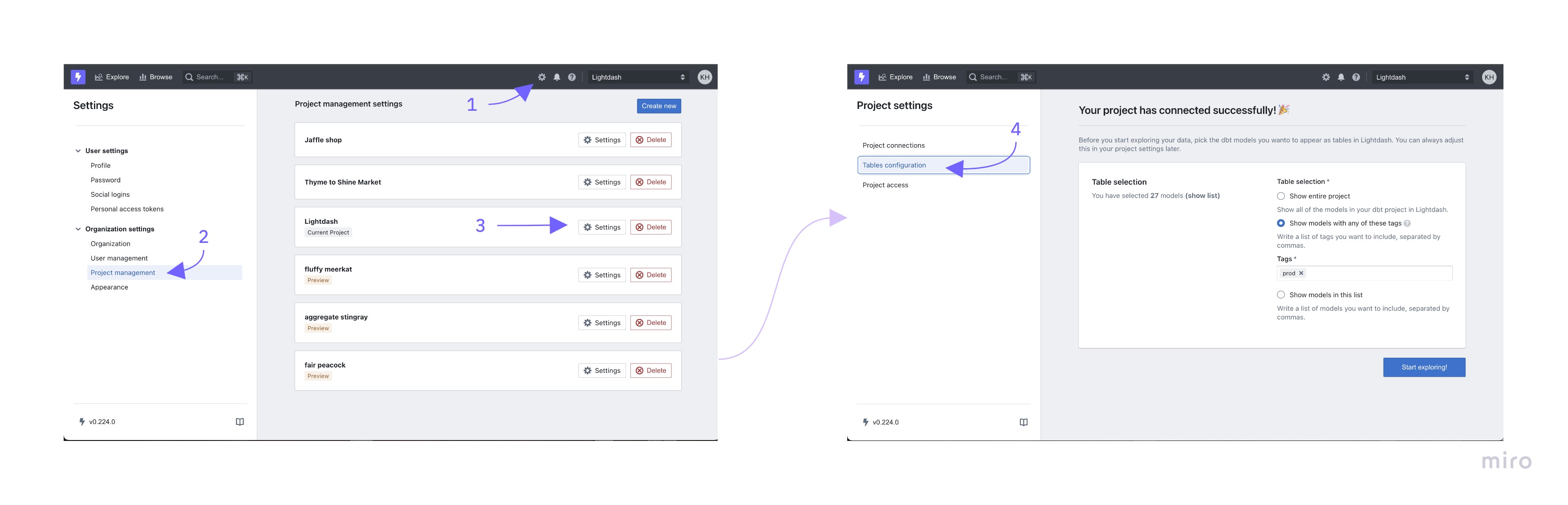
To get to your Table Configuration settings, just:
- Click
Settingsin the navigation bar - Click on
project managementin the sidebar - Click on the
Settingsbutton for the project's tables you want to configure - Once you're in your
Project settings, click on theTables configurationin the sidebar.
Now that you're in the right place, let's get to the juicy stuff. You have three options for configuring the Tables that pop up in Lightdash:
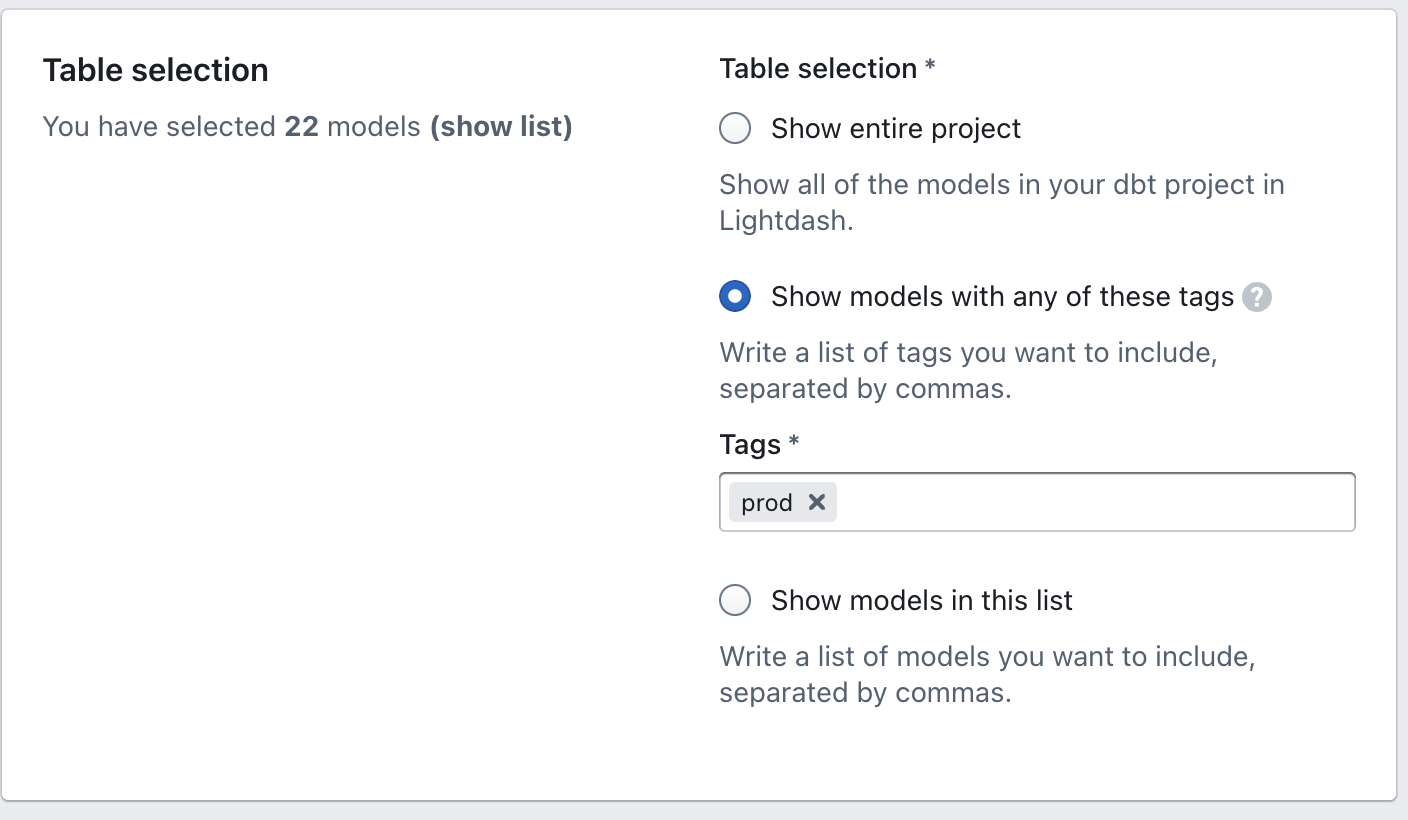
Show entire project: I hope this one isn't too much of a surprise. If you select this option, it shows all of the models with .yml files in your dbt project in Lightdash.
Show models with any of these tags: This option depends on dbt tags. You can learn more about using tags to manage your project here. If you already have a specific model tag (or tags) you want to limit Lightdash to using, this is where you can add them in. For example, all of our production models have the tag
prod, so we've configured our Tables using that tag.Show models in this list: If you're not keen on using tags then you can manually select the models you want to include as Tables in your Lightdash project using this option.
Changing your Table's labels, adding joins, and more!
Once you're happy with which Tables are showing up in Lightdash, you can add configurations to your Tables like:
- Changing how the Table name appears in Lightdash (using the
labelsconfig) - Joining your Table to other Tables (using the
joinsconfig)
All of these configurations and more are outlined in the Tables reference doc here.
👩💻 Advanced tips for managing Tables
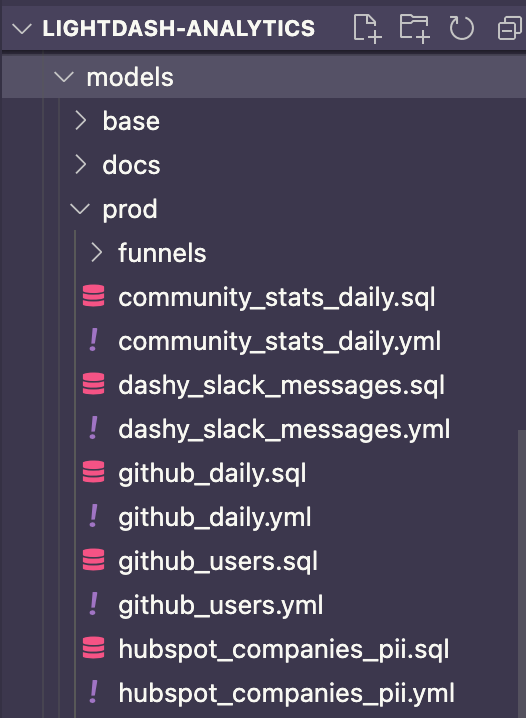
We recommend structuring your dbt project with one .yml file per model (or .sql file).
We've found that this makes it easier to navigate through your .yml files and easier to manage your dbt models, especially as your project becomes bigger.
Here's an example of our dbt project at Lightdash too see what that looks like in practice:
- We have one .sql file per model (these are the files where all of our models' business logic sits)
- We have one .yml file per model (these are the files where all of your Tables' configuration sits)
But, in my dbt project, I have a single schema.yml file. Not one for each model. Will that still work?
Yep! We realize that schema files come in all shapes and sizes.
Some people prefer to write the .yml files for all of their models in a single .yml file at the directory level, and that's totally fine - it will still work with Lightdash.
But, like we said just above, if you're trying to decide how to setup your dbt project, we'd recommend having one .yml file per model.
Limiting the Tables in Lightdash using dbt tags
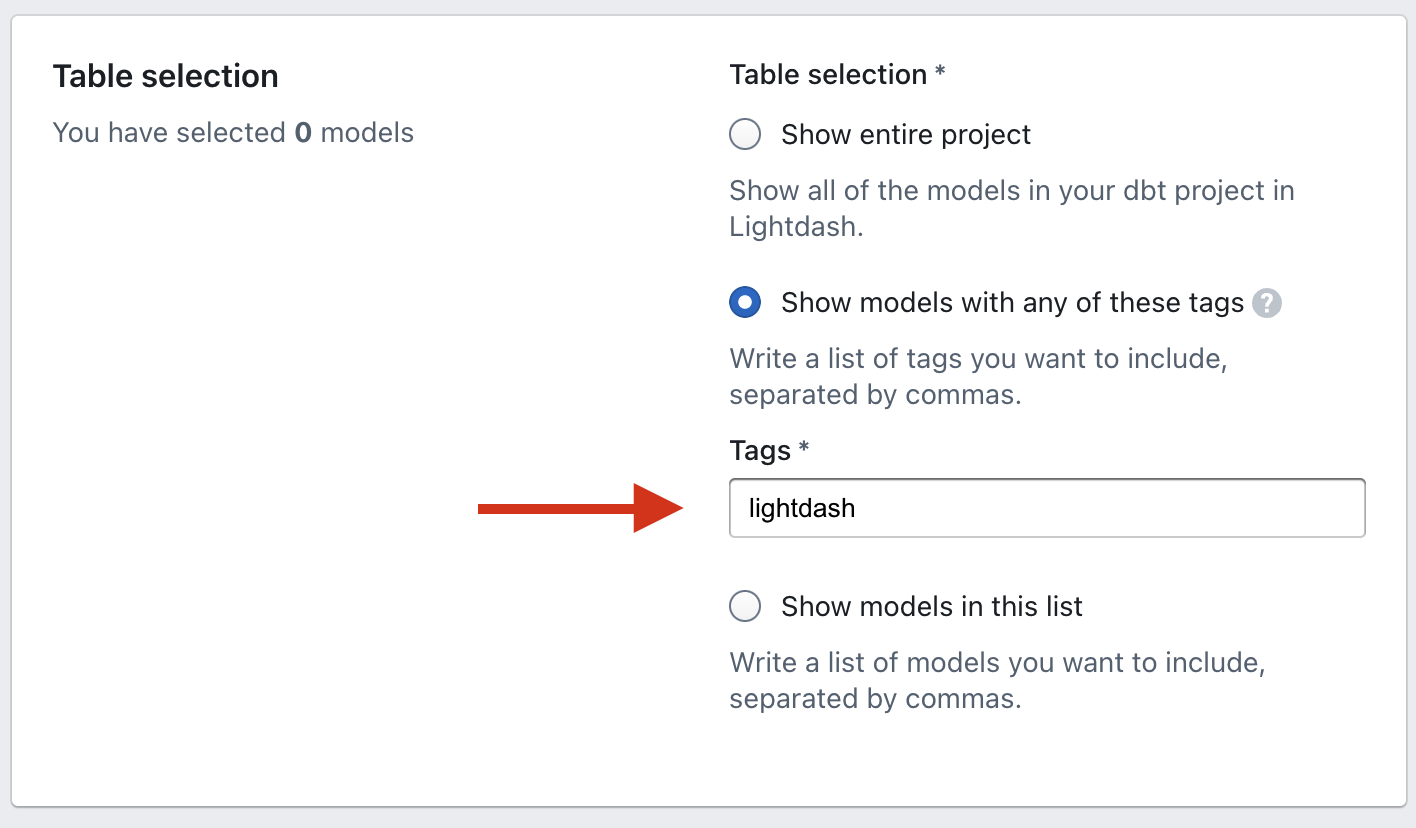
There may be a specific set of models that you want include as Tables in Lightdash. If this is the case, we recommend using dbt's tags to tag these models. You can use sets of existing tags, or you can create a new Lightdash-specific tag.
You can add tags to your model's .yml file like this:
version: 2
models:
- name: model_name
config:
tags: ['lightdash']
Or, to your model's .sql file in the config block:
{{ config(
tags=["lightdash"]
) }}
select ...
Then, you'll set your Table Configuration:
Select the models you want to run using dbt selection syntax
The lightdash dbt run command supports dbt model selection syntax to generate .yml files for a group of models. This means you can use tags or other model selection syntax to specify which models you want to generate dimensions for in your dbt project.
lightdash dbt run -s tag:lightdash # all models with the lightdash tag
lightdash dbt run -s payments # just payments
lightdash dbt run -s payments+ # payments and all children
lightdash dbt run -s +payments # payments and all parents
lightdash dbt run -s payments+ +customers tag:lightdash # mix and match
Generate Tables and dimensions for your entire dbt project in one command
To do this, you just need to run the following on your command line:
lightdash dbt run
This command will run + generate tables for all of the models with .yml files. It will also generate dimensions for all of the columns in your dbt project.