Lightdash Preview
Developer previews are temporary Lightdash projects where you can safely experiment with your metrics, dimensions and charts without affecting your production project.
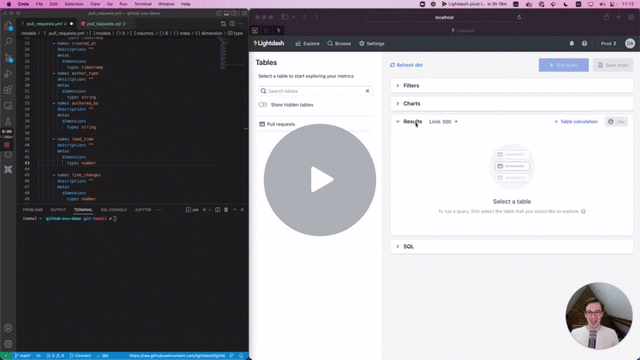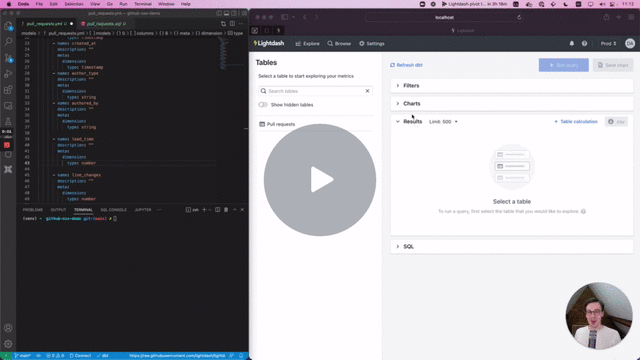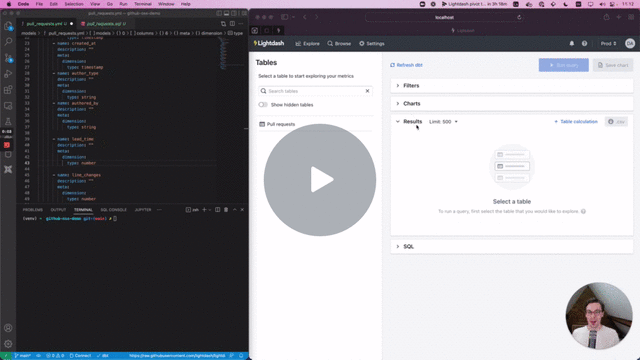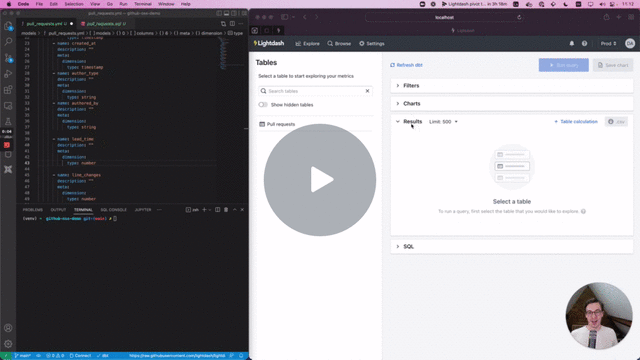
Preview environments will copy all spaces/charts/dashboards into your new preview environment, so you can test the content and also run validation. This is only copied on preview creation, you can't sync the content afterwards.
Run lightdash preview from inside your project
# This will create a preview and will wait until you press a key to delete the preview project
lightdash preview
or
# This will create a preview and exit, you will have to run lightdash stop-preview to delete it
lightdash start-preview
Then cmd + click to open the preview link from your terminal. Once you're in Lightdash go to Explore --> Tables, then click on the model(s) you just updated to see your changes and play around with them.
Problems with credentials?
When you create developer previews, Lightdash will use the same warehouse connection settings you have in your
profiles.yml file for your current dbt project. This can be a problem if you're using a local database that your
laptop can reach but your Lightdash instance cannot.
Set up developer previews on your pull requests
If you've connected Lightdash to GitHub, you can setup a github action and get Lightdash to create new dynamic preview projects automatically
when a new pull request is created, and it will automatically delete the preview project when the pull request is closed or merged.
Step 1: add the credentials to Github secrets
If you haven't already set up a GitHub action for Lightdash, you'll need to add some secrets to GitHub. If you already have a GitHub action for Lightdash, then you can use the same Lightdash secrets you created for your other action.
We are going to add some secrets and config to GitHub actions, but you don't want those to be public, so the best way to do this is to add them as secrets on Github.
If you already have a GitHub action for Lightdash, then you can use the same Lightdash secrets you created for your other action.
Go to your repo, click on Settings , on the left sidebar, click on Secrets under Security. Now click on the New repository secret

We need to add the following secrets:
LIGHTDASH_API_KEY
Create a new personal access token, by going to Settings > Personal Access Tokens. This is the token you'll put in for LIGHTDASH_API_KEY.

LIGHTDASH_PROJECT
The UUID for your project. For example, if your URL looks like https://eu1.lightdash.cloud/projects/3538ab33-dc90-aabb-bc00-e50bba3a5f69/tables, then 3538ab33-dc90-45f0-aabb-e50bba3a5f69 is your LIGHTDASH_PROJECT
LIGHTDASH_URL
This is either https://eu1.lightdash.cloud or https://app.lightdash.cloud for Lightdash Cloud users (check the URL to your Lightdash project).
If you self-host, this should be your own custom domain.
DBT_PROFILES
Some tips for this bit:
- You might be able to copy a bunch of the information from your local
profiles.ymlfile. You can see what's in there by typingcat ~/.dbt/profiles.ymlin your terminal. - If you have a separate
prodanddevprofile, you probably want to use the information from yourprodprofile for your GitHub action.
Find your data warehouse from the list below to get a profiles.yml file template. Fill out this template, and this is your DBT_PROFILES secret.
BigQuery
Step 1: create a secret called GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS
Add the service account credentials (the JSON file) that you want to use for your GitHub action. It should look something like this:
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "jaffle_shop",
"private_key_id": "12345",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- ... -----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "jaffle_shop@jaffle_shop.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "12345",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/jaffle_shop"
}
Step 2: create another secret called DBT_PROFILES
Copy-paste this template into the secret and fill out the details
[my-bigquery-db]: # this is the name of your project
target: dev
outputs:
dev:
type: bigquery
method: oauth
keyfile: keyfile.json # no need to change this! We'll automatically use the keyfile you created in the last step.
project: [GCP project id]
dataset: [the name of your dbt dataset]
More info in dbt's profiles docs: https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/warehouse-profiles/bigquery-profile#service-account-file
Postgres
company-name:
target: dev
outputs:
dev:
type: postgres
host: [hostname]
user: [username]
password: [password]
port: [port]
dbname: [database name]
schema: [dbt schema]
threads: [1 or more]
keepalives_idle: 0
connect_timeout: 10
retries: 1
More info in dbt's profiles docs: https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/warehouse-profiles/postgres-profile#profile-configuration
Redshift
company-name:
target: dev
outputs:
dev:
type: redshift
host: [hostname.region.redshift.amazonaws.com]
user: [username]
password: [password]
port: 5439
dbname: analytics
schema: analytics
threads: 4
keepalives_idle: 240
connect_timeout: 10
ra3_node: true # enables cross-database sources
More info in dbt's profiles docs: https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/warehouse-profiles/redshift-profile#password-based-authentication
Snowflake
my-snowflake-db:
target: dev
outputs:
dev:
type: snowflake
account: [account id]
# User/password auth
user: [username]
password: [password]
role: [user role]
database: [database name]
warehouse: [warehouse name]
schema: [dbt schema]
threads: [1 or more]
client_session_keep_alive: False
query_tag: [anything]
More info in dbt's profiles docs: https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/warehouse-profiles/snowflake-profile#user--password-authentication
DataBricks
your_profile_name:
target: dev
outputs:
dev:
type: databricks
catalog:
[
optional catalog name,
if you are using Unity Catalog,
only available in dbt-databricks>=1.1.1,
]
schema: [schema name]
host: [yourorg.databrickshost.com]
http_path: [/sql/your/http/path]
token: [dapiXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX] # Personal Access Token (PAT)
threads: [1 or more]
More info in dbt's profiles docs: https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/warehouse-profiles/bigquery-profile#service-account-json
Step 2: Create start-preview.yml and close-preview.yml workflows in Github
Go to your repo, click on Actions menu, and click on Configure

Now copy this start-preview.yml file from our cli-actions repo
And save by clicking on Start commit
Do the same with this close-preview.yml file.
You're done!
Everytime you create a new pull request , a new preview project with your branch name will be created on your organization.
Everytime you make a change to that branch, the preview environment will get updated.
Once you close or merge your pull request, the preview project will get deleted.
You can see the log on Github actions page

How to use the developer credentials in your preview project
When developing in dbt, you typically have a different set of credentials and dataset/schema than when you are running in production. Here are two options on how to set them up based on the developer that opened the Pull Request.
If you use dbt cloud IDE to create commits and pull requests you need a few extra steps. We need to add a step in the GitHub action to fetch the user that created the pull request.
- uses: actions/github-script@v6
id: get_pr_creator
with:
script: |
return (
await github.rest.repos.listPullRequestsAssociatedWithCommit({
commit_sha: context.sha,
owner: context.repo.owner,
repo: context.repo.repo,
})
).data[0].user.login;
result-encoding: string
When copying the following templates, you should replace ${{ github.actor }} with ${{steps.get_pr_creator.outputs.result}}.
Using profile targets
Update your DBT_PROFILES to have 1 target per developer. The target name should be their GitHub username.
jaffle_shop:
target: prod
outputs:
prod:
type: bigquery
method: oauth
keyfile: keyfile.json
project: jaffle-shop
dataset: prod
katie: # example developer 1, should be GitHub username
type: bigquery
method: oauth
keyfile: keyfile.json
project: jaffle-shop
dataset: dbt_katie
jose: # example developer 2
type: bigquery
method: oauth
keyfile: keyfile.json
project: jaffle-shop
dataset: dbt_jose
Then, update your GitHub action to use the username as the --target flag for the lightdash start-preview command.
run: lightdash start-preview --project-dir "$PROJECT_DIR" --profiles-dir . --name ${GITHUB_REF##*/} --target ${{ github.actor }}
Using github environments
Setup a GitHub environment for each developer where the secrets are specifically for them. The environment name should be their GitHub username. Then, update your GitHub action to use the username as the environment.
jobs:
preview:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
environment: ${{ github.actor }}
How to use the dbt cloud schema in your preview project
If you are using a continuous integration job in dbt cloud, you can use the schema that is created by dbt cloud (dbt_cloud_pr_<job_id>_<pr_id>) for your preview project.
First we need to add an environment variable to your profile.yml file that will be used by dbt to connect to the correct schema.
schema: "{{ env_var('DBT_SCHEMA') }}"
If you are using BigQuery, it should be dataset instead of schema.
Then we need to add a step in the GitHub action to fetch the pull request id.
- uses: actions/github-script@v6
id: pr_id
with:
script: |
if (context.issue.number) {
// Return issue number if present
return context.issue.number;
} else {
// Otherwise return issue number from commit
return (
await github.rest.repos.listPullRequestsAssociatedWithCommit({
commit_sha: context.sha,
owner: context.repo.owner,
repo: context.repo.repo,
})
).data[0].number;
}
result-encoding: string
After that we need to add a new env variable to the step "Lightdash CLI start preview" which is the schema that dbt cloud will use.
Note that in this example we assume the job id is 1234. You will need to replace this with the actual job id.
env:
# ... keep existing env variables
DBT_SCHEMA: 'dbt_cloud_pr_1234_${{steps.pr_id.outputs.result}}'
Now dbt will use the correct schema when running in the preview environment.